Topology Optimization using Machine Learning
Topology Optimization using Machine Learning
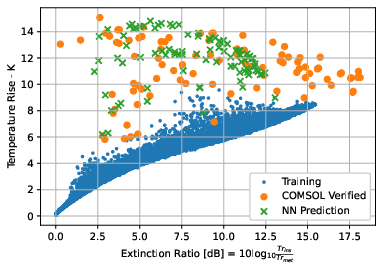
Traditional inverse design approaches can be costly, especially when considering dual objective function problems with multi-physics and multi-timescale considerations. We use a dual neural network optimization algorithm to design a 3D thermal-electromagnetic device (optical shutter). The devices utilize a phase change material (vanadium dioxide) to achieve the shuttering effect. The first neural network (convolutional neural network, CNN) acts as a surrogate model, supplementing the traditional solver calls and making predictions for device performance. This CNN was trained on easy-to-produce, single physics data as opposed to the more costly fully-coupled simulations that would traditionally be required. The second neural network optimizes the design while taking into account given manufacturing limitations (feature size). We show how the reduced computational cost of the trained model allows for generation of an optimized design front (Pareto front), enabling informed optimization of the device.
For more information, please see the following publication: A Dual Neural Network Approach to Topology Optimization for Thermal-Electromagnetic Device Design